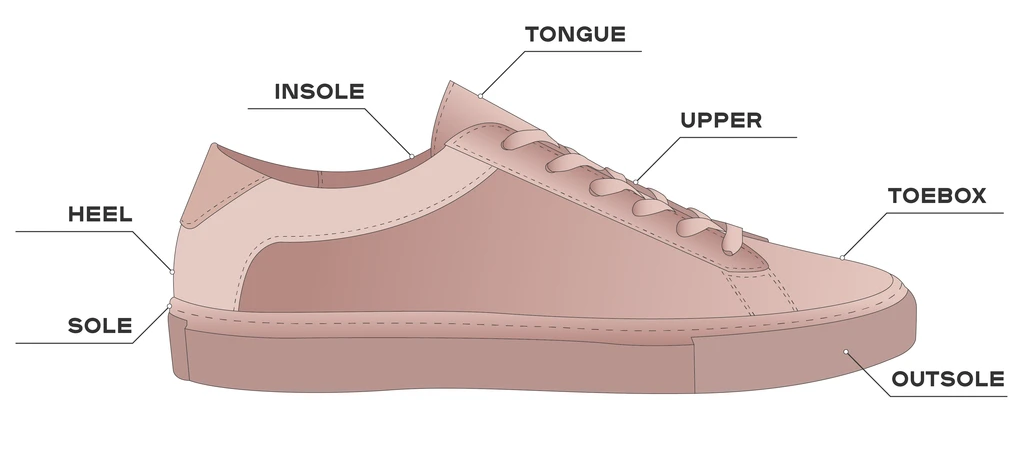
1. Functions of the Midsole
Cushioning: Absorbs impact forces from walking, running, or jumping, reducing strain on the feet and joints.
Support: Provides structural support to the foot, enhancing stability and preventing overpronation or supination.
Energy Return: Some midsole materials return energy from each step, improving overall comfort and efficiency.
Weight Distribution: Helps evenly distribute body weight across the foot for balanced movement.
2. Materials Used
EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate):
Lightweight and flexible material that offers excellent cushioning and shock absorption.
Commonly used in midsoles for a wide range of sneakers due to its versatility and affordability.
Polyurethane (PU):
Durable and dense material that provides firmer support and long-lasting cushioning.
Used in premium sneakers or specific performance models for enhanced durability and responsiveness.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane):
Combines the durability of polyurethane with the flexibility of rubber.
Offers excellent support and stability, often used in high-performance sneakers.
Gel Inserts:
Silicone gel inserts or pods embedded within the midsole for targeted cushioning and shock absorption.
Commonly found in running and athletic sneakers for enhanced comfort and impact reduction.
Air Cushioning:
Air-filled chambers or units integrated into the midsole to provide lightweight cushioning and energy return.
Pioneered by Nike with their Air Max series, now widely adopted across various brands.
3. Design Elements
Density and Thickness: Varies based on the intended use of the sneaker (e.g., running, casual wear).
Heel-to-Toe Drop: The difference in height between the heel and forefoot, influencing stride mechanics and comfort.
Arch Support: Contoured designs or added inserts to support the natural arch of the foot and prevent overpronation.
Flexibility: Grooves or channels in the midsole to allow for natural foot movement and flexibility.
4. Construction Techniques
Compression Molding: Midsoles are molded under high pressure to achieve consistent density and cushioning properties.
Injection Molding: Liquid materials injected into a mold to form the midsole, ensuring precise design and durability.
Foam Blowing: A process where foam expands and solidifies to form lightweight and cushioned midsole materials.
5. Performance and Fashion Integration
Athletic Sneakers: Focus on responsive cushioning, energy return, and stability for optimal performance during sports and activities.
Fashion Sneakers: Blend comfort with stylish designs, using innovative midsole materials and technologies to enhance aesthetic appeal.
Specialized Needs: Some sneakers feature specialized midsoles for specific activities like trail running, basketball, or cross-training, tailored to meet performance requirements.
6. Environmental Considerations
Recycled Materials: Increasing use of recycled EVA or PU materials in midsole construction to reduce environmental impact.
Longevity: Durable midsoles contribute to the overall lifespan of sneakers, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Conclusion
The midsole is a vital component in sneaker design, balancing comfort, support, and performance. Designers must carefully select materials, construction techniques, and design elements to create sneakers that meet the diverse needs of consumers, whether for athletic pursuits or everyday fashion. By integrating innovation and sustainability, sneakers can continue to evolve to meet the demands of a dynamic market while prioritizing comfort and performance.



